Получены полимерные композитные материалы на основе полиэтилена высокой плотности и технического углерода. Исследованы физико-механические и электрические свойства полученных композитов. Обнаружено, что полимерные композиты обладают положительным температурным коэффициентом электрического сопротивления. При этом определено количество технического углерода, необходимое для формирования электропроводящих путей в полимерной матрице. Выявлена зависимость физико-механических и реологических характеристик композитов от содержания технического углерода. Определен концентрационный интервал технического углерода, в котором следует ожидать оптимального сочетания физико-механических, реологических и электрофизических свойств композитов.
Consideration is given to creating the electrically conductive polymeric composites with carboncontaining fillers. Composite materials have been based on high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and technical carbon (TC). Investigation of the electrical properties of the composites showed that the content of the polymer TC in an amount 18 mass. % leads to the formation of conductive mesh which provides “tunneling” of electrons. The conductivity of the resulting composites depends on temperature. The conductivity of the composite HDPE + 18 % TC is reduced with increasing temperature. This is due to the thermal expansion of the polymer matrix which leads to the increase in the distance between the TC aggregates and the rupture of conductive clusters on their basis. Introduction of nanosized additives TC in HDPE leads to a change in its mechanical and technological properties. The modulus of elasticity rises with increasing content of TC regularly grows up to 30 mass. % of TC. Herewith, the composites remain ductile enough up to the concentration TC of the 18 mass. %. The stress of fracture upon stretching and yield strength change simbatically as the content of TC increases with the general tendency to increas. An obvious feature – yield is not observed in the most fragile samples with a filling of 30 mass. % of TC. There is also a local maximum region of stress of fracture and yield strength at 18–25 mass. % TC. The viscosity of the composite material with increasing filler content naturally increases. The rate of the observed increase in the viscosity of the melt of the composition with an increase in the filler content is higher than for strength and plasticity. This is due to the formation of chain structures in a polymer matrix with TC particles.
We defined the NC concentration interval in which we should expect the optimal combination of mechanical, rheological and electrical properties of the composites.
Идентификаторы и классификаторы
- SCI
- Физика
- eLIBRARY ID
- 30484017
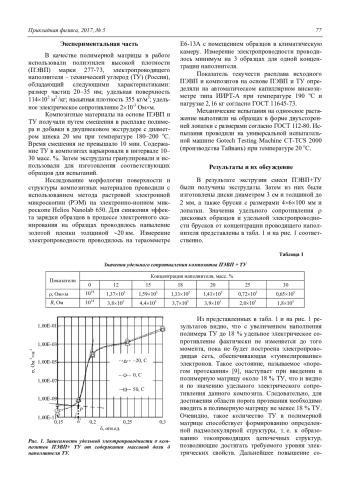
В работе получены электропроводящие полимерные композиты на основе ПЭВП и ТУ. Установлено, что порогу перколяции проводимости соответствует состав композита 18 % TУ. Политермы электропроводности композитов характеризуются высоким значением положительного температурного коэффициента удельного сопротивления, другими словами, последнее указывает на возможность их применения в качестве нагревательных элементов при производстве саморегулирующихся греющих кабелей.
Рассмотрение концентрационных зависимостей некоторых физико-механических и реологических характеристик композитов позволяет определить концентрационный интервал 12–18 масс. % ТУ, в котором следует ожидать оптимального их сочетания с требуемым интервалом электрофизических свойств, важнейшим из которых является электропроводность.
Список литературы
1. Yuichi H., Katsumi S. Japan Patent 2005064090.
2. He Q., Chang A., Xu X. China Patent 1528817.
3. Blok E. J., West J. A. USA Patent 6620343.
4. Wang J., Guo W., Cheng S., Zhang Z. // J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003. Vol. 88. P. 2664.
5. Jong Y. S., Han S. H., Park E. S. // Polym. Comp. 2011. Vol. 32. No. 7. P. 1049.
6. Fang Y., Zhao J., Zha J. W., Wang D. R., Dang Z. M. // Polymer. 2012. Vol. 53. No. 21. P. 4871.
7. Rahaman M., Chaki T. K., Khastgir D. // J. Mater. Sci. 2013. Vol. 48. No. 21. P. 7466.
8. De Rossi D., Veltink P. H. // IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag. 2010. Vol. 29. P. 37.
9. Блайт Т. Р., Блур Д. Электрические свойства полимеров. Пер. с англ. – М.: Физматлит, 2008. Blythe T., Bloor D. Elecctrical Properties of Polymer. Cambridge University Press, 2005.
10. Tang H., Chen X., Tang A., Luo Y. // J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1996. Vol. 59. P. 383.
11. Шиляев П. А., Павлов Д. А., Хохлов А. Ф. // Микросистемная техника. 2004. Т. 3. С. 35.
12. Борукаев Т. А., Китиева Л. И., Машуков Н. И., Микитаев А. К. // Пласт. массы. 1999. № 9. С. 7.
1. H. Yuichi and S. Katsumi, Japan Patent 2005064090.
2. Q. He, A. Chang, and X. Xu, China Patent 1528817.
3. E. J. Blok and J. A. West, USA Patent 6620343.
4. J. Wang, W. Guo, S. Cheng, and Z. Zhang, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 88, 2664 (2003).
5. Y. S. Jong, S. H. Han, and E. S. Park, Polym. Comp. 32 (7), 1049 (2011).
6. Y. Fang, J. Zhao, J. W. Zha, D. R. Wang, and Z. M. Dang, Polymer. 53 (21), 4871 (2012).
7. M. Rahaman, T. K. Chaki, and D. Khastgir, J. Mater. Sci. 48 (21), 7466 (2013).
8. D. De Rossi and P. H. Veltink, IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag. 29, 37 (2010).
9. T. Blythe and D. Bloor, Elecctrical Properties of Polymer (Cambridge University Press, 2005).
10. H. Tang, X. Chen, A. Tang, and Y. Luo, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 59, 383 (1996).
11. P. A. Shilyaev, D. A. Pavlov, and A. F. Khokhlov, J. Nano and Microsystem Technique 3, 35 (2004).
12. T. A. Borukaev, L. I. Kitieva, N. I. Mashukov, and A. K. Mikitaev, International Polym. Sci. and Technology, No. 9, 7 (1999).
Выпуск

С О Д Е Р Ж А Н И Е
ФИЗИКА ПЛАЗМЫ И ПЛАЗМЕННЫЕ МЕТОДЫ
Панов В. А., Василяк Л. М., Ветчинин С. П., Печеркин В. Я., Савельев А. С. Влияние распределенной фазы газовых пузырьков на импульсный электрический разряд в воде 5
Батанов Г. М., Бережецкая Н. К., Давыдов А. М., Кончеков Е. М., Каторгин И. Н., Коссый И. А., Сарксян К. А., Степахин В. Д., Темчин С. М., Харчев Н. К. Плазмохимическая очистка воздуха от городского загрязнения предпороговым разрядом, возбуждаемым пучками микроволн 10
Акишев Ю. С., Петряков А. В., Трушкин Н. И., Устюгов В. А. Улучшение адгезии пенополиуретана к полиэтилену низкого давления, обработанному плазменной струей при атмосферном давлении 20
Панов В. А., Василяк Л. М., Ветчинин С. П., Дешевая Е. А., Печеркин В. Я., Сон Э. Е. Инактивация микроорганизмов на плоских поверхностях барьерным разрядом 25
ФОТОЭЛЕКТРОНИКА
Давлетшин Р. В., Лазарев П. С., Никонов А. В. Исследование неоднородности состава КРТ матричных фотоприемных устройств 31
Будтолаев А. К., Хакуашев П. Е., Чинарёва И. В. Влияние разброса глубины p–n-перехода на параметры лавинных фотодиодов на основе InGaAs/InP 36
Жегалов С. И. Коррекция неоднородности чувствительности матричных фотоприемных устройств с использованием нейронной схемы 42
Будтолаев А. К., Хакуашев П. Е., Чинарёва И. В. Фотодиод на основе GaP для среднего ИК-диапазона 47
Кузнецов П. А., Мощев И. С. Расширение динамического диапазона коротковолновых ИК матричных фотоприемных устройств 52
Средин В. Г., Войцеховский А. В., Ананьин О. Б., Мелехов А. П., Несмелов С. Н., Дзядух С. М., Юрчак В. А. Поверхностные дефекты в эпитаксиальных слоях твердых растворов CdxHg1-xTe, создаваемые мягким рентгеновским излучением 59
Никонов А. В., Яковлева Н. И. Анализ многослойных гетероэпитаксиальных структур на основе CdHgT по спектрам ИК-пропускания 64
ФИЗИЧЕСКОЕ МАТЕРИАЛОВЕДЕНИЕ
Новиков И. К., Крыштоб В. И., Расмагин С. И. Изменение электрических и оптических свойств поливинилхлорида в результате термообработки 71
Борукаев Т. А., Гаев Д. С. Физико-механические свойства композитов на основе полиэтилена высокой плотности и технического углерода 76
Ахмед Б. Б., Нищев К. Н., Пыненков А. А., Моисеев Н. В. Определение термостойкости оптических волокон 82
Буташин А. В., Муслимов А. Э., Колымагин А. Б., Клевачев А. М., Сульянов С. Н., Каневский В. М. Структура пленок AlN, полученных нитридизацией слоев алюминия на сапфировых подложках 87
ФИЗИЧЕСКАЯ АППАРАТУРА И ЕЁ ЭЛЕМЕНТЫ
Татаринова Е. А., Матюхин В. В., Паринов Д. Г. Алгоритм оценки параметров рентгеноконверсионных материалов 92
Супонников Д. А., Булатов З. В., Путилин А. Н., Татаринова Е. А., Дабагов А. Р. Моделирование конверсионных свойств сцинтилляторов для рентгеночувствительных панелей цифровых детекторов 97
Богомолов В. И., Дмитриев Ю. В., Игнатьев Н. Г., Коротков К. Е., Крапива П. С., Москаленко И. Н., Москвичев В. А., Писков С. С. Система передачи аналоговых сигналов на основе модуляторов интенсивности по схеме интерферометра Маха-Цендера для диагностики быстропротекающих процессов 103
ИНФОРМАЦИЯ
XLV Международная Звенигородская конференция по физике плазмы и управляемому термоядерному синтезу 108
Правила для авторов 111
Подписка на электронную версию журнала 114
C O N T E N T S
PLASMA PHYSICS AND PLASMA METHODS
V. A. Panov, L. M. Vasilyak, S. P. Vetchinin, V. Ya. Pecherkin, and A. S. Saveliev Influence of a distributed phase of gas bubbles on the pulsed electrical discharge in water 5
G. M. Batanov, N. K. Berezhetskaya, A. M. Davydov, E. M. Konchekov, I. N. Katorgin, I. A. Kossyi, K. A. Sarksyan, V. D. Ste-pakhin, S. M. Temchin, and N. K. Kharchev Plasma-chemical cleaning of air from the urban pollution by the subthreshold dis-charge excited by microwave beams 10
Yu. S. Akishev, А. V. Petryakov, N. I. Trushkin, and V. A. Ustyugov Improvement of adhesion of polyurethane foam to the low pressure polyethylene processed by a plasma jet at the atmospheric pressure 20
V. A. Panov, L. M. Vasilyak, S. P. Vetchinin, E. A. Deshevaya, V. Ya. Pecherkin, and E. E. Son Inactivation of microorganisms on a plain surface by the barrier discharge 25
PHOTOELECTRONICS
R. V. Davletshin, P. S. Lazarev, and A. V. Nikonov Investigation of heteropeneity of the CdHgTe FPA composition 31
A. K. Budtolaev, P. E. Khakuashev, and I. V. Chinareva Influence of the spread of the depth of the p–n junction on the parameters of InGaAs/InP avalanche photodiodes 36
S. I. Zhegalov Correction of heterogencity of FPA sensitivity by using a neural circuit 42
A. K. Budtolaev, P. E. Khakuashev, and I. V. Chinareva The GaP photodiode for the middle IR range 47
P. A. Kuznetsov and I. S. Moschev Expansion of the dynamic range of short-wave IR FPA 52
V. G. Sredin, A. V. Voitsekhovskii, O. B. Anan’in, A. P. Melehov, S. N. Nesmelov, S. M. Dzyadukh, and V. A. Yurchak Surface defects in epitaxial layers of the CdxHg1-xTe solid solutions created by soft X-ray radiation 59
A. V. Nikonov and N. I. Iakovleva Analysis of CdHgTe multilayer heterostructures on the basis if IR transmission spectra 64
PHYSICAL SCIENCE OF MATERIALS
I. K. Novikov, V. I. Kryshtob, and S. I. Rasmagin Change of electrical and optical properties of polyvinylchloride as the result of thermal treatment 71
T. A. Borukaev and D. S. Gaev Physico-mechanical properties of composites based on high-density polyethylene and technical carbon 76
B. B. Akhmed, K. N. Nishchev, A. A. Pynenkov, and N. V. Moiseev Determination of optical fiber thermostability 82
A. V. Butashin, A. E. Muslimov, A. B. Kolymagin, A. M. Klevachev, S. N. Sulyanov, and V. M. Kanevsky Structure of AlN films formed by nitriding the aluminum metal layers on the (0001) sapphire substrates 87
PHYSICAL APPARATUS AND ITS ELEMENTS
E. A. Tatarinova, V. V. Matyukhin, and D. G. Parinov Algorithm of evaluation of the X-ray conversion materials parameters 92
D. A. Suponnikov, Z. V. Bulatov, A. N. Putilin, E. A. Tatarinova, and A. R. Dabagov Modeling of the conversion properties of scintillators for use in X-ray sensitive panels of digital detectors 97
V. I. Bogomolov, Yu. V. Dmitriev, N. G. Ignatiev, K. E. Korotkov, P. S. Krapiva, I. N. Moskalenko, V. A. Moskvichev, and S. S. Piskov Mach-Zehnder modulator based on the analog signal transmitting system for diagnostics of fast processes 103
INFORMATION
XLV International Zvenigorod Conference on Plasma Physics and Controlled Thermonuclear Fusion 108
Rules for authors 111
Subscription to an electronic version of the journal 114
Другие статьи выпуска
Представлен макет системы передачи аналоговых сигналов сцинтилляционного детектора по волоконно-оптическим линиям связи на основе электрооптических модуляторов по схеме интерферометра Маха-Цендера с использованием технологии частотного уплотнения, оригинального метода определения функции пропускания и рабочей точки модуляторов. Для передачи сигнала одного детектора используются два модулятора, включенные по схеме, близкой к квадратурной. Представлено сравнение результатов передачи сигнала по волоконноопическому и коаксиальному кабелям.
В настоящей работе разработана модель для исследования основных типов конверсионных материалов и алгоритмы ее программирования. Предложенное решение может быть использовано для обеспечения возможности адекватного подбора типа и конструкции сцинтиллятора при решении тех или иных задач, в том числе как средство подбора физикогеометрических характеристик сцинтилляторов, которые позволят обеспечить наилучшие параметры по световыходу и шумности, не ухудшая при этом контраст. Выделены основные элементы преобразовательных стеков. Для моделирования конверсионных материалов и сцинтиллирующих экранов на их базе использовался метод последовательного послойного моделирования, когда взаимодействие между различными слоями преобразовательного стека происходит последовательно от слоя к слою. Представленная модель позволяет решать задачу оптимизации для конкретных применений. Проведены расчеты контрастноэнергетических параметров моделируемых сцинтилляторов. Выполнены эксперименты по проверке адекватности модели. Анализ результатов позволил показать адекватность модели. Предложенная модель исследования сцинтилляторов позволяет производить предиктивную оценку их свойств при разработке рентгеночувствительных панелей.
В настоящей работе выделены основные количественные и качественные характеристики, определяющие информативность и точность передачи изображения объекта контроля при проведении рентгеновских исследований. Перечень характеристик определяется основными требованиями к конверсионным материалам предназначенным для создания рентгеночувствительных панелей, используемых при построении детекторов рентгеновского излучения в цифровых рентгеновских аппаратах различного назначения: для медицинской рентгеновской диагностики, для радиационного неразрушающего контроля в промышленности, контроля пищевых продуктов и т. п. Разработан алгоритм оценки характеристик рентгеноконверсионных материалов. Разработана методика оценки характеристик изображения исследуемого объекта в лабораторных условиях включающая корректировку чувствительности фотосенсора, Gain-калибровку, корректировку дефектных пикселей, получение графиков типовых показателей функции передачи модуляции (MTF) и квантовой эффективности регистрации (DQE). Представленная методика может служить основой для автоматизации процесса оценки характеристик рентгеноконверсионных материалов.
Методами электронографии, электронной и рентгеновской дифракции изучено строение пленок, полученных отжигом в азоте предварительно нанесенных слоев металлического алюминия на (0001) поверхность сапфировых пластин. Пленки нитрида алюминия на подложках сапфира растут, в соответствии с ориентационным соотношением (0001)<10 1 0>AlN║ ║(0001)<11 2 0>Al2O3. Наилучшие результаты были получены при нитридизации алюминиевых пленок на сапфире в режиме нагрева до температуры 1200 °С (со скоростью нагрева ~100 °С/час) и выдержке в течении 1 часа.
С применением методов термического анализа (ТМА, ТГА, ДСК) проведены сравнительные исследования термостойкости полимерных защитных оболочек оптических волокон (ОВ) различных типов. Показано, что совместное использование методов термического анализа позволяет детально исследовать природу физических процессов, протекающих в защитных оболочках ОВ при термическом воздействии, а также определять температурные границы диапазона термической стабильности ОВ.
Проведен сравнительный анализ спектров поглощения растворов и пленок поливинилхлорида, прошедших термообработку. Показаны и объяснены различия характеристик сопряжённых двойных связей углерода в пленках и растворах. Определены удельные сопротивления пленок. Получены результаты о влияние времени термообработки на спектры поглощения и удельное сопротивление экспериментальных образцов поливинилхлорида.
Проведено исследование спектров пропускания многослойных гетероэпитаксиальных структур на основе тройных твёрдых растворов кадмий-ртуть-теллур. Реализована модель расчета характеристик эпитаксиальных слоев, входящих в состав сложной многослойной гетероэпитаксиальной структуры, из экспериментального спектра пропускания. Для вычисления параметров слоев реализован метод пакетного градиентного спуска. Проведен расчет параметров образцов гетероэпитаксиальных структур, выращенных методами жидкофазной и молекулярно-лучевой эпитаксии: определены толщины рабочих фоточувствительных слоев с погрешностью не более 0,1 мкм и состав КРТ с погрешностью не более 1 %. Разработанные модели показывают эффективность для экспресс-контроля оптических характеристик образцов полупроводниковых структур.
Показана возможность селективного поверхностного дефектообразования при облучении мягким рентгеновским излучением эпитаксиальных слоев CdxHg1-xTe за счет избирательного воздействия излучения на отдельные атомы поверхности.
Обосновывается необходимость расширения динамического диапазона в МФПУ коротковолнового ИК-спектра. Традиционно применяемые способы обладают низкой эффективностью, в особенности, в крупноформатных матрицах с шагом не более 15 мкм. Наибольшей эффективностью расширения динамического диапазона (до 100 дБ) обладают накопительные ячейки с индивидуально изменяемой передаточной характеристикой в зависимости от яркости фрагментов наблюдаемой сцены. В данной работе предлагается простой в топологической реализации и эффективный способ расширения динамического диапазона, основанный на автоподстройке времени накопления индивидуально в каждой ячейке интегральной схемы считывания. При этом сохраняется высокая крутизна и линейность преобразования в накопительных ячейках с умеренной освещенностью (до 50–70 % от максимального сигнала), но снижается чувствительность в ячейках, близких к насыщению. В результате формируется линейно-логарифмическая передаточная характеристика, обеспечивающая расширенный динамический диапазон. В работе приводятся примеры полученных изображений с расширенным динамическим диапазоном в коротковолновом ИК-спектре.
Рассмотрена возможность создания диода с барьером Шоттки на GaP с низкой высотой барьера для реализации возможности работы в качестве обнаружителя мощных оптических сигналов в среднем ИК-диапазоне. Были проведены исследования влияния увеличения концентрации носителей заряда в области контакта на высоту барьера. В структуру GaP n- и pтипа проводимости были имплантированы различные ионы при разных дозах и энергиях с последующим отжигом в течении 60 минут при температуре 700 оС в азотной среде. Были исследованы CV-характеристики образцов, по результатам которых были определены высоты барьеров. Полученные результаты подтвердили теоретические расчёты. В работе показано, что необходимое снижение высоты барьера «металл–полупроводник» для сдвига спектральной чувствительности GaP в инфракрасную область, может быть получено путем подлегирования контактной области эпитаксиального слоя n-типа проводимости ионами Si с энергией 100 кэВ и дозой (флюенсом) 41014 см-2 с последующим отжигом имплантированного слоя в течении 60 минут в атмосфере N2 при температуре 700 °С. В качестве барьерного металла может быть использована золотая плёнка, напылённая в вакууме. Результаты исследования показали, что увеличения концентрации носителей заряда в области контакта до значений около 1019 см-3 даёт возможность снижения высоты барьера Au-n-GaP до 0,2 эВ.
Рассматриваются варианты применения нейронной схемы для коррекции неоднородности и дефектов фотоприемных устройств. Анализируются варианты с использованием корректирующих коэффициентов и вариант без коэффициентов. Рассматривается альтернатива микросканера и опорных сигналов. Варианты сопоставляются с коррекцией с использованием для калибровки двух опорных сигналов. Вариант без коэффициентов – нейронная схема формирует выходное сигналы по градиентам входных сигналов. В других вариантах нейронная схема используется для формирования коэффициентов по чувствительности и по смещению. Улучшение коэффициентов достигается распараллеливанием их вычисления. Варианты сопоставляются по коэффициенту корреляции входных и выходных кадров. Совокупные показатели качества вариантов – это наличие микросканирования/опорных сигналов, использование корректирующих коэффициентов, кадровая частота, непрерывность/прерывность работы, корреляция входных и выходных кадров. С увеличением кадровой частоты нейронная схема с использованием микросканера позволяет обеспечить непрерывный режим работы с соизмеримым с двухточечной коррекцией качеством изображения и более простой обработкой.
В данной статье говорится о допустимых отклонениях глубины диффузии, выборе оптимального типа эпитаксиальных структур для изготовления лавинных InGaAs/InP-фотодиодов. При изготовлении ЛФД особое внимание уделяется созданию определённой конфигурации электрического поля в структуре. Конфигурация электрического поля в структуре зависит от исходных параметров структуры и от процессов диффузии. Отклонения от параметров приводят к неработоспособности ЛФД. Было представлено два типа структуры: тип 1 – с равномерным легированием лавинной области (треугольное поле) и тип 2 – с пиковым легированием лавинной области (прямоугольное поле). Указанные эпитаксиальные структуры выращивались методом МОС-гидридной эпитаксии. Типичные параметры структуры типа 1: лавинная область n-InP толщиной 3,9 мкм и уровнем легирования 1,71016 см-3, область поглощения n-InGaAs толщиной 2,35 мкм и уровнем легирования не более 11015 см-3. Типичные параметры структуры типа 2: лавинная область n-InP толщиной 3,6 мкм и уровнем легирования не более 11015 см-3 зарядная область n+-InP толщиной 0,3 мкм и уровнем легирования 8,51016 см-3, область поглощения n-InGaAs толщиной 2,1 мкм и уровнем легирования не более 11015 см-3. В обеих структурах p–n-переход создавался в лавинной области n-InP методом диффузии цинка. Для каждой структуры при различных глубин p–n-перехода, создаваемого диффузией, рассчитывалось напряжение, при котором обеспечивался коэффициент умножения равный 10. Структура типа 1 работоспособна в диапазоне глубин p–n-перехода х0 = (1,77– 2,18) мкм при рабочих напряжениях (56–75) В. Допустимый разброс х0 = 0,41 мкм ( 10 %). Структура типа 2 работоспособна в диапазоне глубин p–n-перехода х0 = (2,50–3,40) мкм при рабочих напряжениях (49–61) В. Допустимый разброс х0 = 0,90 мкм ( 15 %). При изготовлении InGaAs/InP ЛФД структура с пиковым легированием в лавинной области (тип 2) обладает большей технологической устойчивостью по сравнению со структурой с равномерным легированием лавинной области (тип 1). Допустимые отклонения по глубинам p–n-перехода составляют ( 15 %) для структуры типа 2, и ( 10 %) для структуры типа 1.
Проведено исследование пространственной неоднородности спектральных характеристик фоточувствительности матриц фоточувствительных элементов на основе твёрдых растворов кадмий-ртуть-теллур (КРТ) различных форматов. Описана методика исследования спектральных характеристик чувствительности. Приведено распределение длинноволновой границы чувствительности для линейки формата 6576 фоточувствительных элементов (ФЧЭ). Проведен расчёт среднего состава и погрешности измерения состава КРТ для всех элементов линейки. Проведено сравнение вычисления погрешности длинноволновой границы чувствительности выбранного ФЧЭ с значениями границы в локальной области матрицы ФЧЭ. Показана эффективность экспресс-методики контроля качества матриц в части равномерности распределения состава КРТ по площади матрицы.
Экспериментально исследована инактивация споровых микроорганизмов на диэлектрической поверхности барьерным разрядом с плоскими электродами. Показано, что при средней удельной мощности разряда 0,3 Вт/см3 эффективность обеззараживания составляет три порядка за времена экспозиции в интервале 0,5–60 секунд, причем слабо зависит от времени экспозиции.
В данной работе представлены результаты экспериментальных исследований по генерации и свойствам одиночной и множественных плазменных струй, сформированных диэлектрическим барьерным разрядом в потоке атмосферного воздуха. Показано, что применение плазменных струй весьма эффективно для повышения смачиваемости поверхности полиэтиленовых труб и улучшения их адгезионных свойств по отношению к пенополиуретану, широко используемому для теплоизоляции труб, применяемых в жилищно-коммунальном хозяйстве, нефтегазовой промышленности и т. п. Плазменные струи в потоке воздуха представляют большой практический интерес, поскольку замена дорогостоящего инертного плазмообразующего газа на окружающий воздух кардинально упрощает и удешевляет плазменную технологию модификации полимерных поверхностей и открывает возможность ее широкого внедрения в практику.
Приводятся первые результаты использования в качестве основы метода плазмохимической очистки городской воздушной среды от экологически опасных загрязнений подпорогового микроволнового разряда (самоподдерживающегося несамостоятельного (СНС) разряда), возбуждаемого пучком микроволн. Пучок микроволн создаётся гиротронным излучателем, генерирующим одиночные импульсы мощностью 600 кВт, длительностью 20 мс при длине волны 0,4 см. На двух образцах воздуха, изъятых из реальной атмосферы г. Москвы, в лабораторных экспериментах, проведённых в ИОФ РАН, продемонстрирована высокая эффективность одновременного снижения содержания характерных для современного большого города вредных веществ, поставляемых в атмосферу городским транспортом и промышленностью. Предлагаются различные варианты использования СНС-разрядов для решения задач обеспечения экологической чистоты воздушной среды мегаполисов.
Экспериментально исследовано развитие импульсного электрического разряда в воде с паровоздушными микропузырьками, распределение которых в объёме жидкости близко́ к равномерному. Наличие объёмных микропузырьков со средним диаметром 50 мкм при объёмном газосодержании не более 1 % не меняет механизм развития электрического разряда в воде с проводимостью 300 мкСм/см в диапазоне перенапряжений 1–1,5 при значении минимального пробойного напряжения 9 кВ на разрядном промежутке 1 см, причем механизм остаётся тепловым. При указанных условиях определяющую роль играют поверхностные пузырьки, которые приводят к смене наблюдаемого механизма развития разряда. Инициация происходит одновременно на обоих электродах в поверхностных пузырьках, к замыканию промежутка длиной 1 см приводит рост катодного канала со скоростью 60 м/с за время 160 мкс.
Статистика статьи
Статистика просмотров за 2026 год.
Издательство
- Издательство
- АО "НПО "ОРИОН"
- Регион
- Россия, Москва
- Почтовый адрес
- 111538, г Москва, р-н Вешняки, ул Косинская, д 9
- Юр. адрес
- 111538, г Москва, р-н Вешняки, ул Косинская, д 9
- ФИО
- Старцев Вадим Валерьевич (ГЕНЕРАЛЬНЫЙ ДИРЕКТОР)
- E-mail адрес
- orion@orion-ir.ru
- Контактный телефон
- +7 (499) 3749400