The modern theory of development includes such concepts as entropy, dissipative and conservative structures, equilibrium systems, etc. But what is behind these concepts?
Are they not quite correct, which leads to a misunderstanding of the development process? How, on their basis, can a more general process diagram be constructed that would give a complete description of social dynamics?
Идентификаторы и классификаторы
- SCI
- Системология
- eLIBRARY ID
- 88883357
The term and the concept of “entropy” (from Greek. en, trope - rotation, transformation) first introduced the outstanding German physicist, one of the founders of thermodynamics and molecular-kinetic theory of heat, by Rudolf Clausius in 1865. The scientific task that gave rise to this concept was to establish a correspondence between the amount of heat flowing to the object (system) and the change in its temperature. An additional property of heat transfer depending on the degree of “internal ordering” of the system was discovered, which led to the emergence of a new concept of entropy in science. By definition, entropy is a measure of depreciation of energy, its loss, dispersion into the surrounding space, etc. Thus, the term and its content, having a purely physical character, by virtue of its universality, has given rise to a new general paradigm.
Список литературы
1. Dubnishcheva T. Concepts of modern natural science. Textbook / Chapter 4. Concepts of classical thermodynamics and statistical mechanics / The concept of “entropy”. The essence of the dispute about the “thermal death of the Universe”. – Electronic source. Access mode: http://www.gumer.info/bibliotek_Buks/Science/dubn/04.php
2. Korolkov B.P. Thermodynamic foundations of self-organization (monograph). -Irkutsk. IrGUPS. 2011. 120 p.
3. History of science. Conceptual apparatus: Terminological dictionary / comp. N.I. Kobzeva. Orenburg. OSU. 2010. 143 p.
4. Various forms of entropy / Market journal. electronic source. Access mode: http://www.market-journal.com/voprosiupravleniya/2.html
5. Prangishvili I.V. Entropy and other system regularities: Problems of control of complex systems. M. Science. 2003. 428 p.
6. Shitikov V.K., Rozenberg G.S. Biodiversity assessment: an attempt at a formal generalization / Structural analysis of ecological systems. Quantitative methods of ecology and hydrobiology (Collection of scientific papers dedicated to the memory of A.I. Bakanov). Tolyatti. SamNTs RAS. 2005. S. 91-129.
7. Entropy as an indicator of human adaptation to new living conditions / Medical Science / Electronic source. Access mode: http://medscience.asia/articles/entropiya.
8. Entropy and the essence of I.Prigozhin’s theory. electronic source. Access mode: http://www.market journal.com/voprosiupravleniya/9.html
9. Cockshott P., Wright I. Probabilistic approach in economics / Information, money and value. electronic source. Access mode: http://left.ru/2009/2/cockshott184.phtml
10. Yankovsky N.A., Makogon Yu.V., Ryabchin A.M. Innovative and classical theories of catastrophes and economic crises: monograph / Ed. Makogon Yu. V. Donetsk. DonNU. 2009. 331 p.
11. Pushkareva N.V. Postpositivism - Popper, Lakatos, Feyerabend, Kuhn. electronic source. Access mode: http://www.disser.ru/library/70/247.htm
12. Nicolis G., Prigogine I. Self-organization in non-equilibrium systems: from dissipative structures to orderliness through fluctuations. M. Mir. 1979. 512 p.
13. Prigogine I., Stengers I. Order out of chaos: A new dialogue between man and nature: Per. from English / Common. ed. V.I.Arshinov, Yu.L.Klimontovich and Yu.V.Sachkov. M. Progress. 1986. 432 p.
14. Dissipative structure. Stages of formation of dissipative structures (self-organization). electronic source. Access mode: http://solidstate.karelia.ru/~KOF/OLD/kse-pact/lectures/text/glava9_1.html
15. “Chemical pendulum” - Belousov-Zhabotinsky reaction. electronic source. Access mode: http://sota.ee/forum/index.php PHPSESSID=7aff34735b80bef3b696ce782de9a05d&topic=625
16. Prigogine I. Introduction to thermodynamics of irreversible processes. M. Publishing house of foreign literature. 1960. 128 p.
17. IDEF0 functional modeling methodology. Guidance document IDEF WP 0-2000. M. Gosstandart of Russia. 2000. 75 p.
Выпуск

The role of visco-plastic friction at various moments of inertia for layered planets is considered using the example of the Earth, and the role of tidal friction is analyzed using the example of Jupiter’s moons.
The phenomenon of strange attractors is presented
The article is devoted to the problem of the evolution of the biosphere, the issues of its origin, organization, factors and patterns are considered.
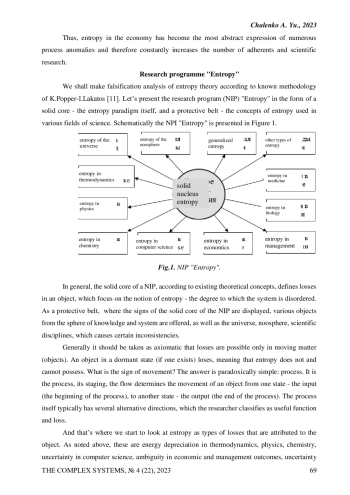
The modern theory of development is analyzed, and it is shown how a more general process scheme can be constructed that would give a complete description of social dynamics.
The role of nonlinear language in the formation of a new nonlinear worldview that has created a new nonlinear-synergetic paradigm of modern science
Другие статьи выпуска
The huge role of a non-linear language in the formation of a new non-linear worldview, which created a new non-linear-synergetic paradigm of modern science, is shown. First, the development of this language induced the development of nonlinear dynamics and its formation as a new science. Secondly, this language has enriched many sciences with such concepts as “deterministic chaos”, “strange attractor”, “dissipative structures”, “fractal”, “bifurcation”, which have now become general scientific. Thirdly, this language formed the basis of a new “non-linear” thinking. Fourth, the non-linear language, which is especially attractive to young scientists, has contributed to the influx of new talented scientists into non-linear dynamics. All of the above played a decisive role in the formation of a new general scientific non-linear paradigm, impossible and inconceivable without a new language. It is thanks to this language that modern scientists look at the world with a “nonlinear vision”, not imagining a linear reality, incomparably enriching their ideas about everything that exists and develops. So, eidetically varying the concept of “chaos”, outlined the range of systems that allow chaotic behavior, found out the methodological principles for the study of such systems, determined the characteristic features of chaotic development, and thus passed the “second stage” of the phenomenological analysis of deterministic chaos.
The work is devoted to the problem of biosphere evolution. Questions of the origin of the biosphere, its organization, factors and patterns of evolution are considered. Particular attention is paid to the influence of man on the atmosphere.
Having non-linear equations share properties is useful, but when it comes to measurements and calculations, every non-linear system is a thing in itself. Comprehension of one of them gave absolutely nothing for penetration into the other. The Lorenz attractor revealed the stability and hidden structure of a system that, otherwise, seemed completely unstructured. But how could this double helix help specialists study objects that have nothing to do with it? No one knew.
The discoverers of new forms compromised the rigor of the scientific style. Ruelle wrote: “I have not mentioned the aesthetic impact of strange attractors. These tangles of curves and swarms of dots sometimes conjure up magnificent fireworks or mysterious galaxies, sometimes they resemble a bizarre riot of plants. Before us is a vast realm of undiscovered forms and unknown perfection.
In the light of the latest research on the role of tidal friction and excess infrared emission of the giant planets of the solar system the role of viscous friction at different moments of inertia for a layered planets for example Earth
Издательство
- Издательство
- ИФСИ
- Регион
- Россия, Москва
- Почтовый адрес
- 140080, Московская область, г. Лыткарино, ул. Парковая, Д. 1, офис 14/А
- Юр. адрес
- 140080, Московская область, г. Лыткарино, ул. Парковая, Д. 1, офис 14/А
- ФИО
- Старцев Вадим Валерьевич (ГЕНЕРАЛЬНЫЙ ДИРЕКТОР)
- E-mail адрес
- systemology@yandex.ru
- Контактный телефон
- +7 (963) 7123301