The ongoing digital transformation provides an infrastructural basis for multi-level networking. The United States and China as the leaders in designing long-term social and economic development strategies pay serious attention to technological sovereignty and sustainable interaction between the corporate and public sectors that are impossible without reliable digital infrastructure. Digital platforms have become its most important component, creating prerequisites for the formation and development of various network structures. The paper discusses the subordinate effects resulting from the development of digital platforms as part of digitalization. Today, global value chains are being transformed, changing the global reproduction system; the reproduction process is also influenced by digital transformation; technological development and innovations bring new opportunities and transform all aspects of socioeconomic interaction. The methodological basis of the study is constituted by the system approach, comparative analysis and statistical methods. The paper examines the prospects of digital platforms in the PRC both for the national economy and international cooperation and proposes guidelines on their strategic development. It describes the specific features of financing their formation and systematizes the characteristics of networking in the sphere of e-commerce, cloud services and investment cooperation. Addressing the social aspect of using digital platforms, the study emphasizes the importance of social monitoring and migration controls that give the country a competitive advantage in developing and testing the technologies involved. It also shows that platform employment and digital poverty create multidirectional trends affecting the country’s economic development.
Идентификаторы и классификаторы
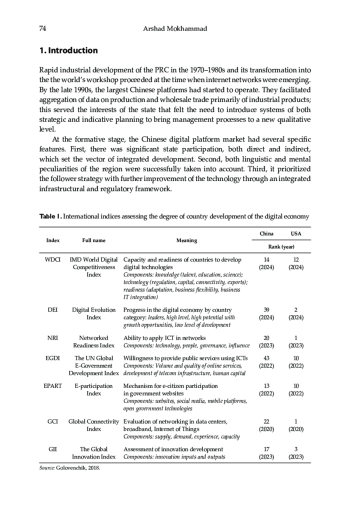
Rapid industrial development of the PRC in the 1970–1980s and its transformation into the the world’s workshop proceeded at the time when internet networks were emerging. By the late 1990s, the largest Chinese platforms had started to operate. They facilitated aggregation of data on production and wholesale trade primarily of industrial products; this served the interests of the state that felt the need to introduce systems of both strategic and indicative planning to bring management processes to a new qualitative level.
Список литературы
- Antipina, O.N. (2020). Platforms as multilateral markets of the digitalization era. World Economy and International Relations, 64(3), 12–19. (In Russian). https://doi.org/10.20542/0131-2227-2020-64-3-12-19
- Baden-Fuller, C., & Mangematin, V. (2013). Business models: A challenging agenda. Strategic Organization, 11(4), 418-427. https://doi.org/10.1177/1476127013510112
- BCS-Express. (2023). Alibaba. Recovery of domestic demand. https://bcs-express.ru/novosti-i-analitika/alibaba-vosstanovlenie-vnutrennego-sprosa
- Belretail. (2021). The share of e-commerce in China’s retail sales will exceed 50% in 2021. https://belretail.by/news/dolya-e-commerce-v-roznichnyih-prodajah-v-kitae-prevyisit-v-godu
- Bobkov, V.N., & Chernykh, E.A. (2020). Platform Employment: Scales and Signs of Instability. The world of the new economy, 14(2), 6–15. (In Russian). https://doi.org/10.26794/2220-6469-2020-14-2-6-15
- Buck, A. (2024). eCommerce Market Size by Country. MobiLoud. https://www.mobiloud.com/blog/ecommerce-market-size-by-country Companies Market Cap. (2024). Largest Chinese companies by market capitalization. https://companiesmarketcap.com/china/largest-companies-in-china-by-market-cap/
- Danilin, I.V. (2019). The development of the digital economy of the United States and the PRC: factors and trends. Contours of global transformations: politics, economics, law, 12(6), 246–267. (In Russian). https://doi.org/10.23932/2542-0240-2019-12-6-12
- Digital Russia. (2018). The Digital Economy Subcommittee approved the definition of digital platforms. https://d-russia.ru/na-podkomissii-po-tsifrovoj-ekonomike-odobrili-opredelenie-tsifrovyh platform.html
- Dini, P., Iqani, M., & Mansell, R. (2011). The (im)possibility of interdisciplinarity: lessons from constructing a theoretical framework for digital ecosystems. Culture, Theory and Critique, 52(1), 3–27. https://doi.org/10.1080/14735784.2011.621668
- Eckhardt, J.T., Ciuchta, M.P., & Carpenter, M. (2018). Open innovation, information, and entrepreneurship within platform ecosystems. Strategic entrepreneurship journal, 12(3), 369–391. https://doi.org/10.1002/sej.1298
- Fehrer, J.A., Woratschek, H., & Brodie, R.J. (2018). A systemic logic for platform business models. Journal of Service Management, 29(4), 546–568. https://doi.org/10.1108/JOSM-02-2017-0036
- Gasparenienea, L., Remeikienea, R., & Schneiderb, F. (2015). The factors of digital shadow consumption. Intellectual Economics, 9(2), 108–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intele.2016.02.002
- Gawer, A., & Cusumano, M. (2014). Industry platforms and ecosystem innovation. Journal of Product Innovation Management, 31(3), 417–433. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpim.12105
- Geliskhanov, I.Z., Yudina, T.N., & Babkin, A.V. (2018). Digital platforms in the economy: essence, models, development trends. Scientific and Technical Vedomosti SPbSPU. Economic Sciences, 11(6), 22–36. (In Russian). https://doi.org/10.18721/JE.11602
- Gershman, M., Klypin A., Ivanova, I., & Bredikhin, S. (2022). China’s Science and Technology Policy: Toward Global Leadership. HSE. https://issek.hse.ru/news/688845347.html
- Golovenchik, G.G. (2018). Rating analysis of the level of digital transformation of the EAEU and EU economies. Digital Transformation, 2(3), 5–18. (In Russian).
- Hein, A., Schreieck, M., & Riasanow, T. (2019) Digital platform ecosystems. Electronic Markets, 30, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12525-019-00377-4 HSE. (2021). Digital ecosystems. https://hsbi.hse.ru/articles/tsifrovye-ekosistemy/ International Trade Administration. (2023). China — eCommerce. https://www.trade.gov/country-commercial-guides/china-ecommerce
- Ivanova, I., Demidkina, O., & Privorotskaya, S. (2023). China: top 15 technology trends in digital transformation. HSE. https://issek.hse.ru/news/860964524.html
- Israilova, E.A., & Balanova, M.M. (2020) On the role of the state in regulating the activities of platform companies by the example of the PRC. Bulletin of Rostov State University of Economics, 2(70), 191–198. (In Russian).
- Johnson, M.W., Christensen, C.M., & Kagermann, H. (2008). Reinventing your business model. Harvard Business Review, 86 (12), 57–68.
- Katz, M.L., & Shapiro, C. (1985). Network externalities, competition, and compatibility. The American economic review, 75(3), 424–440.
- Kheyfets, B.A. (2020). What route will Russia take along one difficult Chinese path: Scientific report. Institute of Economics of the Russian Academy of Sciences
- Kovalev, A.A., & Knyazeva, E.Yu. (2021). The system of social credit in the PRC: the experience of political science analysis. State and Municipal Management. Academic Notes, 1, 191–198. (In Russian). https://doi.org/10.22394/2079-1690-2021-1-1-191-198
- Lee, S., Kim, H., Kim, J., & Choi, J. (2019). China’s Internet Plus Strategy: Characteristics and regional case study. KIEP: World Economy Brief, 9(23), 1–5.
- Li, W., Badr, Y., & Biennier, F. (2012). Digital ecosystems: challenges and prospects. In proceedings of the international conference on management of Emergent Digital EcoSystems, 117–122.
- Maslov, A.A. (2021). Dynamics of internal migration and the problem of development of northeastern regions of China in 2010–2020. Population, 24(3), 135–150. (In Russian). https:// doi.org/10.19181/population.2021.24.3.11
- Moazed, A., & Johnson, N. L. (2016). Modern Monopolies: What It Takes to Dominate the 21st Century Economy. St. Martin’s Publishing Group.
- Mootee, I. (2008). What’s the difference between platform strategy vs. business strategy vs. product strategy? FutureLab. https://www.futurelab.net/blog/2008/05/whats-difference-betweenplatform- strategy-vs-business-strategy-vs-product-strategy Nexus Group. (2024). Alibaba Cloud. https://www.nexusgroup.com/partner/alibaba-cloud
- Nielsen, C., & Lund, M. (2014). An introduction to business models. In The basics of business models, 8–20.
- Parker, G. G., Van Alstyne, M. W., & Choudary, S. P. (2016). Platform Revolution: How Networked Markets Are Transforming the Economy and How to Make Them Work for You. W. W. Norton & Company.
- Polozhikhina, M. A. (2018). National models of digital economy. ESPR, 1, 111–154 (In Russian).
- Rochet, J.-C., & Tirole, J. (2003). Platform Competition in Two-Sided Markets. Journal of the European Economic Association, 1(4), 990–1029. https://doi.org/10.1162/154247603322493212
- Rochet, J.-C., & Tirole, J. (2011). Must-take cards: merchant discounts and avoided costs. Journal of the European Economic Association, 9(3), 462–495. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1542- 4774.2011.01020.x
- Selin, A. (2016). Digital business models: the main trend of the modern market. Digest of news of the world of high technologies, 5, 1–14. (In Russian).
- Solomatina, A. R. (2021). Digital Silk Road as a component of the initiative “One Belt - One Road”. Post-Soviet Studies, 4(4), 296–307. (In Russian). https://doi.org/10.24412/2618-7426-2021-4-296- 307
- Srnicek, N. (2017). Platform Capitalism. Cambridge: Polity Press.
- Statcounter Global Stats. (2024). Search Engine Market Share China. https://gs.statcounter.com/search-engine-market-share/all/china
- TAdviser. (2023). Cloud services (China market) https://www.tadviser.ru/index.php/Статья:Облачные_сервисы_(рынок_Китая)
- TAdviser. (2024a). Tencent. https://www.tadviser.ru/index.php/Компания:Tencent_Holdings
- TAdviser. (2024b). Censorship (control) on the Internet. China’s experience. https://www.tadviser.ru/index.php/Статья:Цензура_(контроль)_в_интернете._Опыт_Китая
- Wang, X., Lin, X., & Spencer, C. (2019). Exploring the effects of extrinsic motivation on consumer behaviors in social commerce: Revealing consumers’ perceptions of social commerce benefits. International Journal of Information Management, 45, 163–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2018.11.010
- World Economic Forum. (2019). Explained role of China’s state-owned companies. https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2019/05/why-chinas-state-owned-companies-still-have-a-key-role-to-play/
- Zhang, L., & Chen, S. (2019). China’s Digital Economy: Opportunities and Risks. Bulletin of International Organizations, 14(2), 275–303. (In Russian). https://doi.org/10.17323/1996-7845-2019-02-11
- Zuboff, S. (2015). Big Other: Surveillance Capitalism and the Prospects of an Information Civilization. Journal of Information Technology, 30, 75–89. https://doi.org/10.1057/jit.2015.5
- Zuo, M. (2024). China’s gig workers becoming new normal, but ‘inevitable trend’ comes with a burden. South China Morning Post. https://www.scmp.com/economy/economic indicators/article/3269601/chinas-gig-workers-becoming-new-normal-inevitable-trend-comes-burden
Выпуск
Другие статьи выпуска
The paper presents an empirical study of the relationships between financial development, economic growth, urbanisation and energy consumption in the Southern African Development Community for the years 1980 to 2023. The researchers applied the Bayesian approach via Metropolis-Hasting and Gibbs samples as the MCMC methods, and Dumitrescu and Hurlin (2012) and Diagnostic tests to check the causality among all the variables in question and accuracy of the data and model. Over time, there has been a significant positive correlation between financial development, economic growth, industrialization, urbanization, and energy consumption. The results of the Granger causality test showed a unidirectional causal relationship between financial development, urbanization, and energy consumption supporting the alternative hypothesis that there is a relationship between financial development and energy consumption in the Southern African Development Community. It has been found that there is a Bi-directional (feedback) Granger causal relationship between economic growth and energy consumption in the Southern African Development Community; this also supports the alternative hypothesis. The results align with endogenous growth theory, which emphasizes that economic growth is driven by internal factors such as capital accumulation, innovation, and improved efficiencies, where energy plays a significant role. This also supports the view that energy infrastructure development is vital for sustaining economic growth in the region. The diagnostic tests confirm that the model is correct.
This paper examines the sharing economy as an advanced model of interaction between economic agents that helps them mitigate resource constraints and rapidly meet producers’ and consumers’ needs in the face of new challenges. We found the benefits of collaborative consumption, or sharing, to be largely determined by the level of trust in society, development of technological base and adaptation of legal framework to digital transformation of the national economy. Based on the evidence from Russia and Brazil, we classify the factors that determine the sharing economy development and identify effective instruments of regulating sharing relations. The results indicate that regulatory “sandboxes” appear to be most appropriate as they allow participants to test innovations of substantial public importance that lie outside the scope of existing legislative norms.
This study investigates how small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) achieve and manage innovative ambidexterity through their dynamic capability, addressing potential imbalances in changing environments under resource constraints. Employing a comparative case study approach, the research draws on qualitative, in-depth interviews with CEOs and founders of four Russian SMEs operating in the Information Technology (IT) sector, selected from a larger cohort. Key capabilities were identified for each phase of the dynamic capability process. In the sensing phase, essential capabilities include cultivating dynamic technological and marketing skills, problem-solving proficiency and commitment to continuous learning with real-time awareness. In the seizing phase, the emphasis shifts to enhancing capabilities through learning, fostering innovation-driven culture, empowering employees, providing continuous training, promoting active collaboration at all levels, and recognizing achievements through team rewards. During the reconfiguration phase, adaptive decision-making, resource and coordination flexibility and future-oriented innovation and partnerships become critical. These capabilities contribute to a balance of exploratory and exploitative innovation within SMEs enabling the achievement of innovative ambidexterity. Throughout this process, potential imbalances are managed by leveraging critical capabilities such as clear goal-setting and performance feedback, culture of openness, trust, and mutual support, and adaptive decision-making with wise allocation of firm-specific resources. Through our findings, we advance the understanding that ambidexterity is achievable for resource-constrained SMEs in uncertain environment under external constraints, offering insights into dynamic capabilities that enable such attainment.
The paper explores the role of external mentoring as a strategic talent attraction tool in the context of talent shortages and describes the ways in which it can help firms to find new candidates, especially among young graduates, at the same time developing its own employees. The authors conducted 21 in-depth interviews with experienced mentors from multinational companies in Russia and one expert interview. Content analysis was used to identify the key themes related to the effectiveness of external mentoring. External mentoring significantly enhances employer branding, knowledge exchange, learning and professional development. The critical components of success are voluntary participation, non-monetary recognition and long-term trust-based relationships between mentors and mentees. The paper also identifies the challenges that external mentoring may encounter and essential criteria for selecting mentors and mentees. The authors conceptualize external mentoring as a novel approach to talent attraction extending beyond internal employee development. The study provides fresh insights into resolving talent shortages and creating external talent pools, thus contributing to talent management and mentoring literature.
The Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) has garnered significant attention over the past decade. This expansive project promises lucrative opportunities and a potential boost to global trade. However, infrastructure, policy, and strategic challenges pose risks to its international success. This study examines the forces driving the growth of e-commerce supply chain companies participating in the BRI, focusing on China and Russia as research context. Using the Value Chain theory, we explain how combination of its primary and support activities influences the development of international supply chains within the BRI. We employ a multilinear regression model to test the proposed framework, with an ANOVA model to verify the robustness of our findings. The results reveal that primary and support activities have different significance within BRI collaboration. Exogenous factors, particularly industrial and municipal policies, as well as infrastructural development, are the key drivers of e-commerce success in the BRI supply chains. This study contributes to the growing body of literature on the BRI by providing empirical evidence of the factors influencing e-commerce growth in participating countries. Our findings offer insights for firms and policymakers seeking to capitalize on the opportunities presented by the BRI and highlight the areas requiring attention to ensure its long-term viability and success.
Stabilizing the Consumer Price Index (CPI) to protect the populace from the adverse effects of inflation necessitates appropriate measures at both political and economic governance levels. This study examines the impacts of imports (IM) and exports (EX) on inflation (CPI) in Afghanistan using data from 1990 to 2023. The findings from the Autoregressive Distributed Lag (ARDL) model indicate that both IM and EX significantly impact CPI in the short and long term. A robustness check employing the Kernel-based Regularized Least Squares (KRLS) machine learning technique further validates these results. The analysis confirms that international trade has a substantial and positive effect on CPI. Additionally, in the context of Afghanistan, political instability acts as a positive moderator, amplifying the influence of imports and exports on inflation. The study concludes that the country requires a reevaluation of its policies regarding exchange rates and economic growth to mitigate the negative effects of imports, exports, and political volatility on the stability of the CPI.
This research aims to investigate the influence of stock market volatility and liquidity turnover on returns in the emerging markets of Middle East and North Africa (MENA countries) using the interaction of global economic policy uncertainty index and exchange rate as a moderating variable. The paper employs panel quantile regression with daily data from January 1, 2000 to August 30, 2024 and a panel quantile regression sensitivity analysis. The findings suggest that the U. S. economic policy uncertainty index was markedly negative; the negative and significant interaction coefficient between the variables of exchange rate fluctuations and worldwide economic policy uncertainty indicates that stock returns of the MENA markets dropped substantially in response to international economic policy uncertainty; the more extensively the exchange rate fluctuated, the lower were the returns. Empirical evidence reveals shifting dynamics in the impact of short-term interest rate volatility on returns as we move from the period before the pandemic outbreak to the post-pandemic era. The study has notable implications for financial investors. Markets’ response to interest rate volatility cannot be predicted with high degree of certainty because the market reacts spontaneously to adjustments in the short-term interest rate even when market players operate rationally and base their decisions on all available information regarding stock prices. As a result, investors may choose to consider selecting shorter-life alternative equities as a long-term hedge against interest rate volatility risk. The MENA countries’ central monetary authorities and governments should work jointly to maintain stock market stability by enacting measures to make stock exchanges and the equity markets more resilient to the negative effects of uncertainty brought on by foreign economic policy, even as exchange rate volatility rises. Additionally, international business entities and traders could also shield themselves against international economic policy-related risk of uncertainty in the midst of currency volatility given the current research.
This paper concerns Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) employer branding and its impact on employee attraction and retention, seeking to systematize academic knowledge about their interconnections and links to other important management issues. We made a systematic literature review focusing on empirical papers published in academic journals over the last 10 years, which enabled us to identify the directions of contemporary research, commonly used methodologies and contexts explored. It shows that CSR initiatives are increasingly recognized as a critical dimension of employer branding. Alignment of CSR practices and employer branding strategies is essential for attracting top talent. We also observed a strong link between CSR and employer attractiveness, career development, organizational identification, corporate reputation and person-organization fit, which underscores the multifaceted nature of CSR employer branding. It has been found that CSR researchers predominantly use quantitative methodologies in their studies and tend to explore the firms that work in the IT industry. The paper discusses the current state of CSR employer branding research and outlines possible avenues for future studies.
The paper investigates the relationship between corporate governance and organizational performance in Nigeria’s banking sector between 1996 and 2023, using the Tobin-Q valuation and operating performance methodology (quantitative characteristics) of variables in analyzing data collected from secondary sources.
The internal mechanisms of corporate governance such as Returns on Assets (ROA), shareholder profit and Debt-Equity ratio had a negative impact on organizational performance. The study into forecast and long-term co-integration relationship between corporate governance mechanisms and organizational performance has shown that the enhancement of organizational performance by corporate governance mechanisms is likely to experience a steady increase after 2023.
Economic landscape of Pakistan is determined by an extremely complex interaction of domestic and global forces; navigating it successfully requires a clear understanding of its character. The paper explores the dynamic relationships between macroeconomic variables and GDP growth in Pakistan using the Autoregressive Distributed Lag (ARDL) model and other stability tests using time series data from 1980 to 2022. The analysis includes variables representing GDP per capita, inflation, imports, total debt as a percentage of GDP, total population, and forestry and agricultural output. The correlation matrix shows a positive association between GDP growth rate and GDP per capita, total debt service is inversely correlated with total population, and GDP demonstrates a significant negative correlation. The ARDL results indicate that GDP per capita and the agriculture and forestry sectors are significant drivers of economic growth. Over the period in question, inflation only marginally affected GDP growth showing how important it is to maintain price stability through effective policies. Imports provide short-term benefits by enhancing productivity through capital goods and technology inflows but they may pose long-term challenges due to trade imbalances. The influence of population growth appears to be ambivalent: in the short term it contributes to economic growth by increasing labor supply and consumption; in the long term, however, its effect may become detrimental owing to resource constraints. Public debt shows little influence in the short term but negatively impacts growth over time by increasing the fiscal burden of debt servicing. These findings suggest that to achieve long-term economic stability and growth, the country needs targeted policy interventions that should help it control inflation, manage the debt sustainably, optimize imports, and invest in agriculture, which is an important determinant of GDP growth. Future research should concentrate on sector-specific studies and the effects of political stability on economic growth in order to provide deeper insights contributing to Pakistan’s sustainable economic development.
Статистика статьи
Статистика просмотров за 2025 - 2026 год.
Издательство
- Издательство
- МГУ
- Регион
- Россия, Москва
- Почтовый адрес
- оссийская Федерация, 119991, Москва, Ленинские горы, д. 1
- Юр. адрес
- оссийская Федерация, 119991, Москва, Ленинские горы, д. 1
- ФИО
- Садовничий Виктор Антонович (РЕКТОР)
- E-mail адрес
- info@rector.msu.ru
- Контактный телефон
- +7 (495) 9391000
- Сайт
- https://msu.ru/